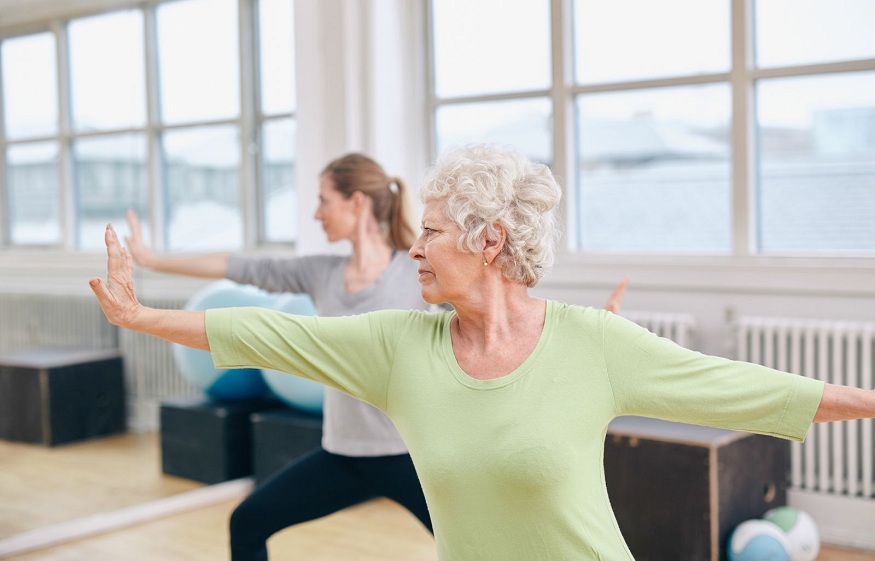

Aerobic exercises, such as running, walking or swimming, can strengthen your heart and lower your risk for developing cardiovascular disease.
These types of exercises also help improve your mood, boost your energy levels and activate your immune system. Cardio exercise is one of the best ways to improve your cardiovascular health and lower your risk of disease.
Aerobics
Aerobic exercise increases the amount of oxygen that your body takes in and uses to keep your heart working. It also increases the size and number of your body’s microscopic powerhouses, called mitochondria. These changes improve how your cells use oxygen to create energy, according to Dr. Jonesco.
In addition, aerobic exercise reduces stress on your heart and helps your arteries work better to carry blood to your organs, reducing the risk of heart disease. It can lower blood pressure and help you control your blood sugar, too.
You can build your aerobic exercise capacity over time by gradually adding new physical activities, increasing the distance, time, or difficulty of your existing ones. Start with brisk walking or low-impact exercises such as jogging, and work your way up to longer workouts over days or weeks.
Strength Training
Strength training, or weight training, involves using resistance and force to overload a group of muscles in order to increase strength, endurance, size or shape. This can be achieved through the use of different forms of equipment including gym equipment and free weights.
A typical strength training workout comprises a number of exercises – each targeting a different muscle group – performed two or three times a week. Perform a warm-up before each strength training session, which consists of about five minutes of activity such as jogging, cycling or skipping to increase heart rate and blood flow through the muscles.
It’s important to use a proper technique when lifting weights; it helps prevent injury and improves performance. Start with lighter weights and progress as your body and confidence level improves – aiming to do at least 12 repetitions (reps) per set.
Interval Training
Interval training is a workout that involves short bursts of exercise (work intervals) followed by longer periods of rest (recovery intervals). They’re a great way to spice up your routine and push yourself harder than you could in a continuous effort.
In addition to helping you build endurance and burn calories, intervals also increase your heart’s ability to deliver oxygen to your muscles. This boost in peak oxygen consumption is linked to a healthier heart and a longer life, says Healthpoint Clinic exercise physiologist Amanda Bonikowske.
You can incorporate intervals into any cardiovascular exercise, including running, cycling, stair-climbing, swimming and walking. If you’re using a treadmill, for example, start with a slow jog and increase your speed in each high-intensity interval until your breathing gets heavy, then return to brisk walking.
Water Exercises
Water aerobics are a top exercise for improving your cardiovascular health. It’s a great low-impact workout that gets your heart rate pumping, and it can improve your flexibility too!
Many people with arthritis and other joint conditions find that water exercise is easy on their joints. It’s also beneficial for pregnant women and overweight people.
Because water is about 1,000 times more resistant than air, it helps build muscle strength and endurance throughout the body. Water exercises can increase your heart rate to help you burn calories and tone your muscles, which can lead to weight loss.
Swimming is a popular exercise for older adults to help keep them fit and active without putting too much pressure on their joints. Repeated workouts in the pool can reduce the stiffening of blood vessels, a common cause of high blood pressure as you get older.
 From Lab to Lifestyle: How the Science of Quality Assurance in Manufacturing Reliable Supplements Protects Consumers and Businesses
From Lab to Lifestyle: How the Science of Quality Assurance in Manufacturing Reliable Supplements Protects Consumers and Businesses  Top Myths About Pediatric Home Health Care Debunked
Top Myths About Pediatric Home Health Care Debunked  Immunity IV Drips – Your Frontline Defense Against Modern-Day Fatigue, Illness, and Burnout
Immunity IV Drips – Your Frontline Defense Against Modern-Day Fatigue, Illness, and Burnout  Is Vasectomy Painful? What Men Should Know about the Procedure
Is Vasectomy Painful? What Men Should Know about the Procedure  Low Blood Oxygen? These 5 Shocking Causes Might Be Putting You at Risk!
Low Blood Oxygen? These 5 Shocking Causes Might Be Putting You at Risk!  Cardiologists And The Approach To Pediatric Heart Conditions
Cardiologists And The Approach To Pediatric Heart Conditions  The Best Practices For Maintaining Healthy Gums In Willow brook
The Best Practices For Maintaining Healthy Gums In Willow brook