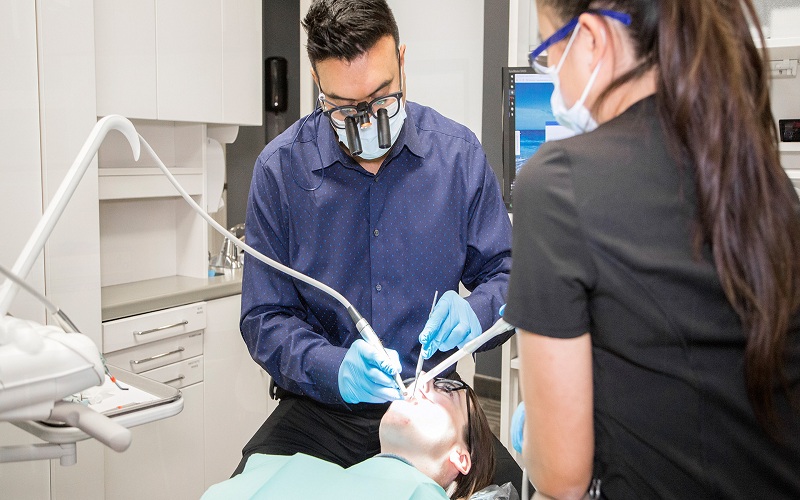
Antibiotic treatment in dentistry is a crucial aspect of patient care, aimed at preventing and treating infections that can arise from dental procedures or existing oral health conditions. Antibiotics are medications that kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms, such as bacteria and are used to treat a wide range of dental infections. The family dentist in Columbia, MD, and their team make use of antibiotics to help restore oral health when needed.
What are the types of dental infections?
Types of dental infections:
- Abscesses: Pus-filled pockets that form in the gums or teeth.
- Cellulitis: Infections of the skin and underlying tissues.
- Endocarditis: Infections of the heart valves.
- Osteomyelitis: Infections of the jawbone.
- Periodontitis: Infections of the gums and supporting tissues.
What are the indications of antibiotic treatment?
Indications for antibiotic treatment in dentistry include:
- Severe infections: Such as abscesses, cellulitis, or osteomyelitis.
- High-risk patients: Patients with compromised immune systems, heart disease, diabetes, or respiratory disease.
- Surgical procedures: Antibiotics may be prescribed before and after surgical procedures to prevent infection.
- Dental implants: Antibiotics may be used to prevent infection around dental implants.
- Periodontal disease: Antibiotics may be used to treat periodontitis, especially in severe cases.
- Endodontic infections: Antibiotics may be used to treat infections related to root canals.
- Facial infections: Antibiotics may be used to treat infections of the face, such as facial cellulitis.
- Bone infections: Antibiotics may be used to treat osteomyelitis (bone infections).
- Joint infections: Antibiotics may be used to treat infections of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
- Soft tissue infections: Antibiotics may be used to treat infections of the soft tissues, such as the tongue, lips, or cheeks.
- Post-extraction infections: Antibiotics may be used to prevent or treat infections after tooth extraction.
- Pericoronitis: Antibiotics may be used to treat infections around impacted teeth.
- Dental trauma: Antibiotics may be used to prevent or treat infections related to dental trauma.
- Oral surgery: Antibiotics may be used to prevent or treat infections related to oral surgery.
What are the common antibiotics used in dentistry?
Types of antibiotics used in dentistry include:
- Penicillin: Effective against a wide range of bacteria.
- Amoxicillin: Similar to penicillin, but more effective against certain bacteria.
- Metronidazole: Effective against anaerobic bacteria, commonly used to treat periodontitis.
- Clindamycin: Effective against a wide range of bacteria, including those resistant to penicillin.
How are antibiotics administered in dentistry?
Administration of antibiotics in dentistry can be done through various routes, including:
- Oral antibiotics: Taken by mouth, usually in pill or liquid form.
- Topical antibiotics: Applied directly to the affected area, such as:
- Antibiotic mouthwashes
- Antibiotic gels or ointments
- Antibiotic powders or sprays
- Intravenous antibiotics: Administered through a vein, usually in severe cases or for patients with compromised immune systems.
- Intramuscular antibiotics: Injected into a muscle, usually for severe infections.
- Subgingival antibiotics: Placed directly into the periodontal pocket, usually for periodontal infections.
- Local antibiotic delivery systems: Sustained-release devices that deliver antibiotics directly to the site of infection.
- Antibiotic-impregnated materials: Materials like bone grafts or dental implants coated with antibiotics to prevent infection.
It’s important to note that antibiotics should only be administered under the guidance of a dental professional, and patients should follow the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment to ensure effectiveness and minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance.
General instructions
- Use antibiotics only when necessary.
- Choose the appropriate antibiotic for the specific infection.
- Follow the recommended dosage and duration of treatment.
- Monitor patients for side effects and antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic treatment in dentistry is a vital aspect of patient care, aimed at preventing and treating dental infections. While antibiotics are effective, their overuse or misuse can lead to serious consequences. Dentists must use antibiotics judiciously, following best practices to ensure optimal treatment outcomes and minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance.

 The Best Practices For Maintaining Healthy Gums In Willow brook
The Best Practices For Maintaining Healthy Gums In Willow brook  Transform Your Smile: Top Cosmetic Dentistry Treatments for Every Age
Transform Your Smile: Top Cosmetic Dentistry Treatments for Every Age  Choosing the Right Family Dentist: What to Look For
Choosing the Right Family Dentist: What to Look For  Choosing the Right Family Dentist: What to Look For
Choosing the Right Family Dentist: What to Look For  Understanding The Difference: When To See A Cosmetic Dentist Vs. An Orthodontist
Understanding The Difference: When To See A Cosmetic Dentist Vs. An Orthodontist  Transform Your Smile: The Importance Of Cosmetic Dentistry
Transform Your Smile: The Importance Of Cosmetic Dentistry  From Lab to Lifestyle: How the Science of Quality Assurance in Manufacturing Reliable Supplements Protects Consumers and Businesses
From Lab to Lifestyle: How the Science of Quality Assurance in Manufacturing Reliable Supplements Protects Consumers and Businesses  Top Myths About Pediatric Home Health Care Debunked
Top Myths About Pediatric Home Health Care Debunked  Immunity IV Drips – Your Frontline Defense Against Modern-Day Fatigue, Illness, and Burnout
Immunity IV Drips – Your Frontline Defense Against Modern-Day Fatigue, Illness, and Burnout